2 The Sources of International Law (p. 20) 1. Introduction International law provides a normative framework for the conduct of interstate relations. In this sense, international society is no exception to the maxim of ibi societas, ibi ius: where there is social structure, there is law. The sources of international law define the rules . . . Read more
(p. 3) 1 Introduction ‘Then felt I like some watcher in the skies When a new planet swims into his ken…’ Keats1 1. Development of the Law of Nations The law of nations, now known as (public) international law,2 developed out of the tradition of the late medieval ius gentium.3 Through an influential series of writers— . . . Read more
(p. 115) 4 Subjects of International Law 1. Introduction1 A subject of international law is an entity possessing international rights and obligations and having the capacity (a) to maintain its rights by bringing international claims;2 and (b) to be responsible for its breaches of obligation by being subjected to such claims.3 This definition, though conventional, . . . Read more
ENFORCEMENT (1) Overview 7.01 (2) General Principles of Enforcement 7.03 Valid Decisions Should Be Summarily Enforced 7.03 Errors of Fact and/or Law: Answering the Right Question the Wrong Way 7.05 Challenges Based on Excess Jurisdiction or Breach of Natural Justice 7.08 Fraud 7.09 Reservation of Position 7.10 Enforcement of Non-pecuniary . . . Read more

CHALLENGES BASED ON BREACH OF NATURAL JUSTICE (1) Summary of Challenges Based on Breach of Natural Justice 10.01 (2) General Principles of Natural Justice 10.02 Materiality of Breach 10.07 Adjudicators’ Decisions Should Generally Be Enforced 10.10 The Adjudicator’s Conduct Is Key 10.12 Impact of the Human Rights Act 1998 10.13 . . . Read more

JURISDICTIONAL CHALLENGES (1) General Principles 9.01 Source and Nature of the Adjudicator’s Jurisdiction 9.01 Jurisdiction to Consider any Available Defences Raised 9.07 Expanding the Adjudicator’s Jurisdiction During the Adjudication 9.09 Adjudicator’s Investigation of Jurisdiction 9.11 Reservation of Rights 9.14 (2) Matters Giving Rise to Jurisdictional Challenge 9.16 No Jurisdiction at . . . Read more

EFFECT OF AN ADJUDICATOR’S DECISION (1) Overview 6.01 (2) General Effects of an Adjudicator’s Decision 6.02 Private between the Parties 6.03 Temporarily Binding until Final Determination 6.05 Time for Compliance 6.08 Final Determination 6.11 Finality by Agreement 6.16 Contractual Finality Provisions 6.19 Effect of the Decision in Subsequent Adjudications 6.24 . . . Read more

SECTION 108 AND THE RIGHT TO ADJUDICATE (1) Introduction 3.01 Changes Made by the 2009 Act 3.05 (2) Issues Arising Out of s. 108(1) 3.07 Disputes Arising under the Contract 3.10 Side Agreements 3.15 Dispute under More than One Contract 3.16 Identity of Contracting Party 3.20 Contract Formation 3.21 Incorporation . . . Read more

AD HOC REFERENCES AND ADJUDICATIONS OUTSIDE THE ACT (1) Ad Hoc References to Adjudications 5.01 Express Agreements to Confer Jurisdiction 5.07 Implied Agreements to Confer Jurisdiction 5.08 Objecting and Reserving the Right to Object 5.09 No Conferral of Jurisdiction where Continued Jurisdiction Objection 5.14 General Reservations 5.16 Key Cases: Ad . . . Read more

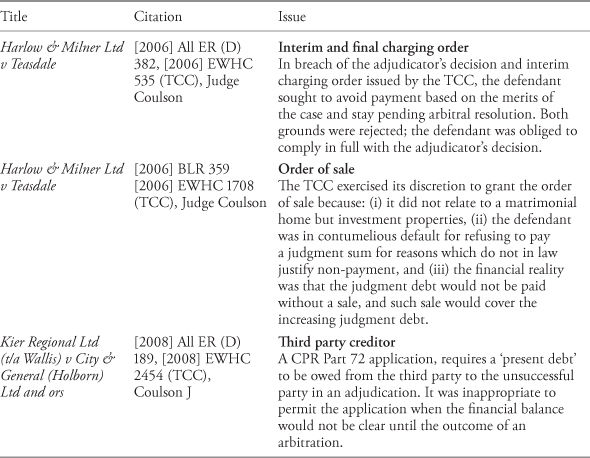
STAYING ENFORCEMENT (1) Introduction 8.01 (2) Stay of Execution of Enforcement Order on Grounds of Impecuniosity 8.05 Insolvency Rules 8.06 Principles of Stay of Execution 8.10 Types of Financial Hardship 8.12 Evidencing the Impecuniosity 8.16 Circumstances in which a Stay Is Unlikely to Be Granted 8.20 Key Cases: Stay of . . . Read more






